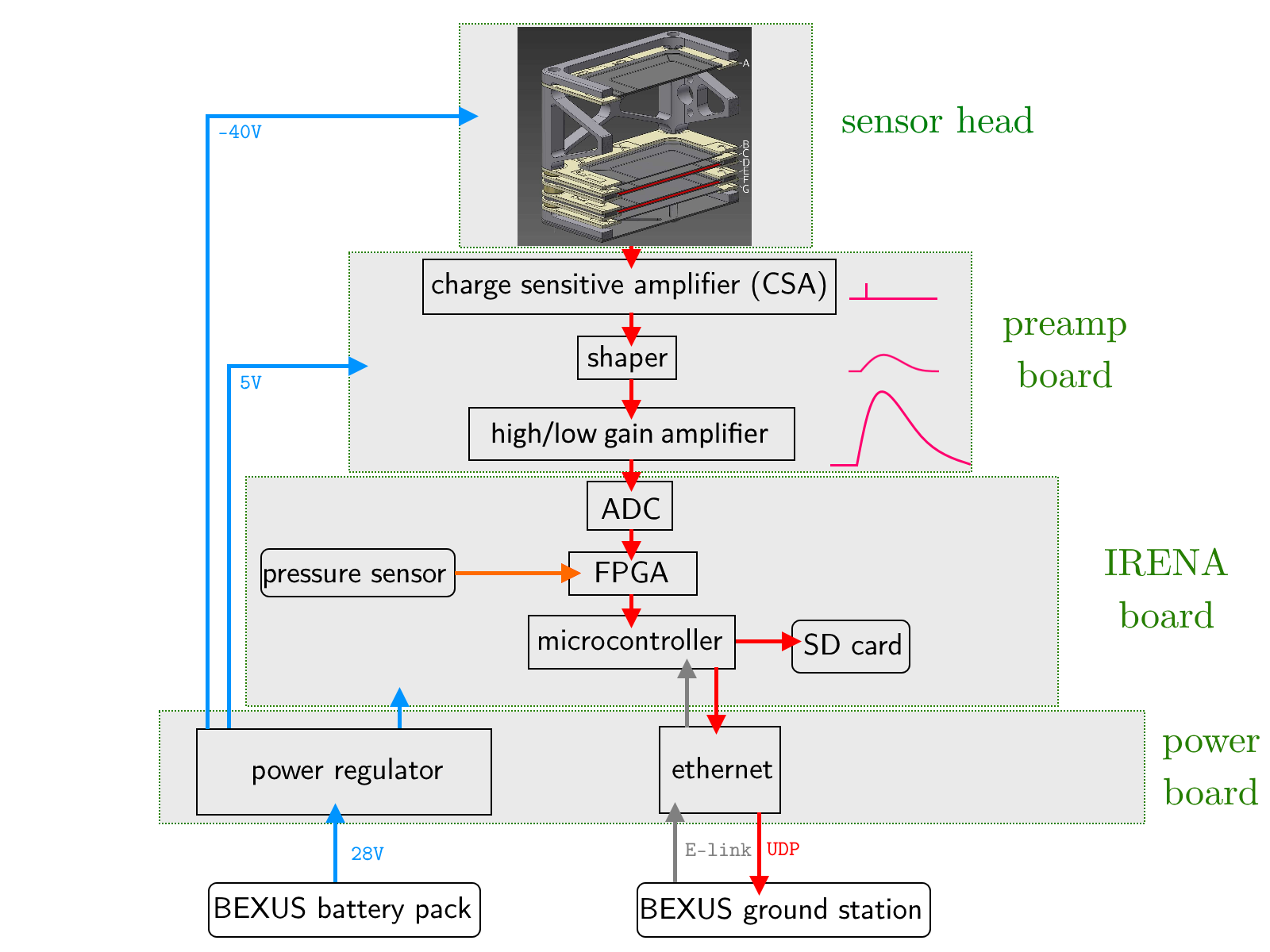
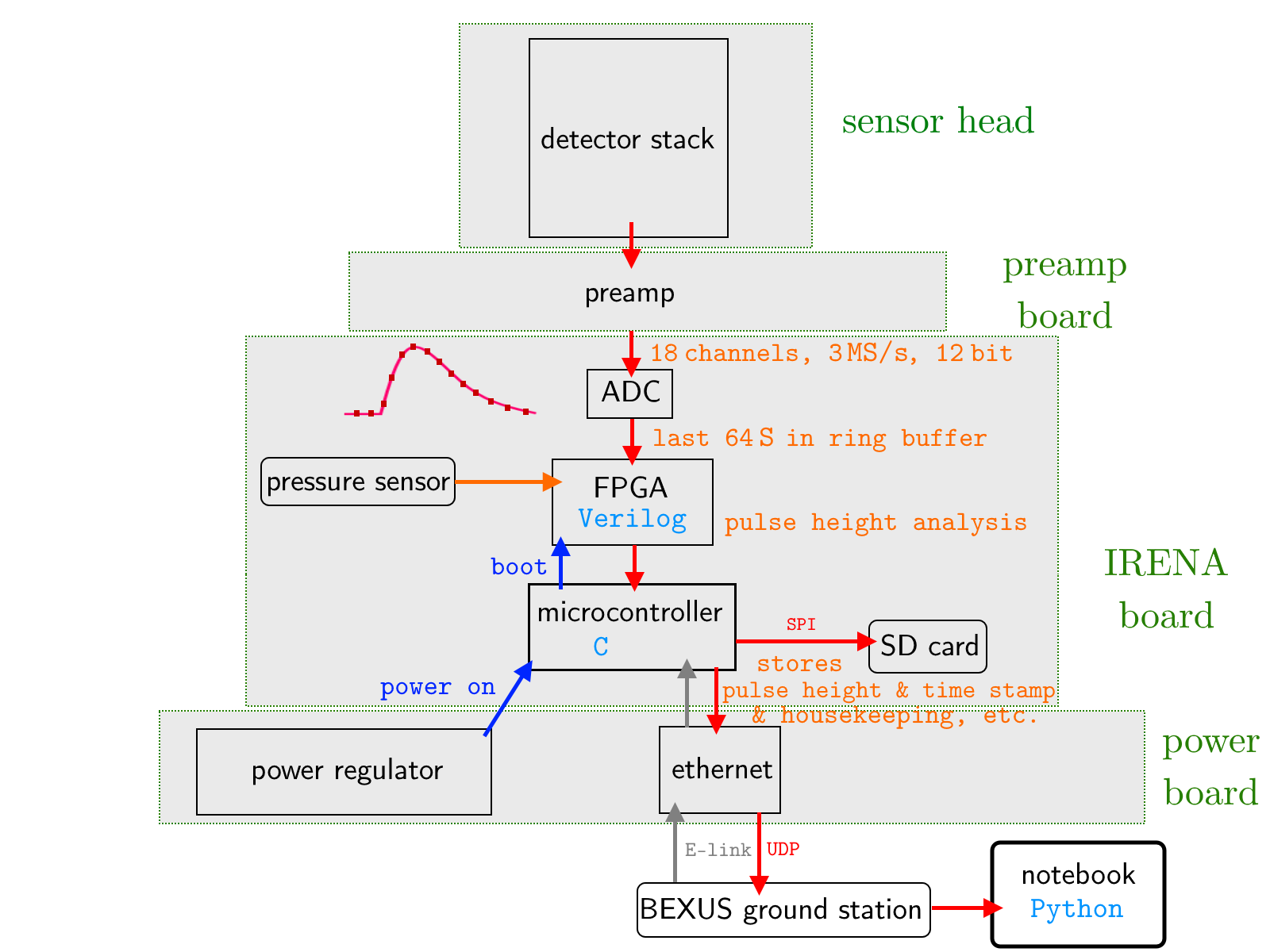
Our TANOS Experiment
The main objective of our Thermal Atmospheric Neutron Observation System (TANOS) is to measure the flux of thermal neutrons in the stratosphere, as there are only few existing measurements. Due to galactic cosmic rays interacting with atmospheric particles, secondary neutrons are generated. Those are moderated to thermal energies through elastic scattering. These resulting neutrons are very slow, with an energy of 0.025 eV. The flux of secondary particles is the largest at a height of about 20 km, the so called Pfotzer maximum. In order to measure these low energy neutrons we developed an instrument consisting of a silicon detector stack and two layers of gadolinium foil between two detectors. The cross section of gadolinium is very high for thermal neutrons, around 49000 barn, thus this material is particularly suitable for the experiment.